A Business Engineer is a hybrid between a business administration and technology expert, a person with the business acumen and engineering abilities to understand a complex organization, devise solutions, and work as a liaison between commercial and technical teams.
A glance at the Business Engineering world
At its core, a business engineer is a hybrid between a business person and an engineer. The business engineer is someone with an understanding of how the business world works at a macro level, combined with how organisms function at a micro level, that can architecture solutions based on several key elements.
As pointed out in Osterle, H. (1995), Business in the Information Age:
The business engineering concept enables the transformation of enterprises from the industrial age into the information age by means of procedure models, methods, and tools
Some of the key elements comprising business engineering require a deep understanding of several disciplines and areas:
- Business model
- Business processes
- Organizational structure
- Digitalization
- Information process and technologies
- The interaction between people and technologies within organizations
In one of its vacancies for Business Intelligence Engineer Amazon defines it as someone that can help “improve and define the best way of doing things throughout the company using the power of your analysis, technical skills, and business acumen.”
While this particular role is focused on improving internal processes to “identify opportunities to improve and optimize ship costs.”
As pointed out by Amazon “the successful candidate will be able to retrieve, integrate, visualize and present critical data in a format that is immediately useful to improve the business decision-making process.”
A discipline between business administration and technology
Business engineering is a discipline in between business administration and technology. As more and more organizations are innovated by combining technological product and processes with remixing old and new business model patterns, it becomes critical to understand and drive those processes.
A business engineer is a manager that can guide companies through hard decisions by looking at quantitative data, navigating ambiguity and reducing the noise where needed. Some of the disciplines part of business engineering are:
A business engineer is a hybrid between a commercial and technical role. It can work as a liaison between commercial and technical teams to device complex solutions to its organizations or other companies for which the business engineer partners with.
What tasks a business engineer performs?
Some of the job descriptions from Indeed and LinkedIn say:
Developing sales and service with regional and global accounts, supporting Account Managers and business development. Driving sales-related activities, implementing customer projects such as product and prototype selections, costing, pricing, quotations, preparation for serial production, and logistics setups.
For instance, among the task required:
- Interacting with customers and consulting with Account Managers providing technical and commercial support
- Applying financial analysis to evaluate business opportunities
- Coordinating and driving customer-related and internal projects and activities
- Supporting and training the organization in technical, commercial and market-oriented tasks
- Handling claims with internal partners and managing quality control
On a position for Business Intelligence Engineer Amazon points out:
- Design, develop and maintain scaled, automated, user-friendly systems, reports, dashboards, etc. that will support business needs
- Partner with operations/business teams to consult, develop and implement KPI’s, automated reporting/process solutions and data infrastructure improvements to meet business needs
- Apply deep analytic and business intelligence skill to extract meaningful insight and learning from large and complicated data sets
- Serve as liaison between the Business and technical teams to achieve the goal of providing actionable insights into current business performance, and ad hoc investigations into future improvements or innovations. This will require data gathering and manipulation, synthesis and modeling, problem-solving, and communication of insights and recommendations
What kind of background, education, and experience do you need to become a business engineer?
For some of the open vacancies for Business Engineer, the required background is:
- Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical or Chemical Engineering or comparable technical field.
- Preferably up to 3 years’ experience in technical sales and knowledge of heat transfer and thermodynamics
- Advanced Microsoft Office with an understanding of calculation tools.
- Experience of CRM/ERP systems is an advantage
Skills:
- Enjoy working in an international environment
- Proactive, positive, and target-oriented team player with a keen interest in technical and commercial matters
- Very strongly customer-oriented
- Strong networker with good interpersonal skills and the ability to cooperate and communicate with many different layers and cultures
Those, of course, are just some of the skills required. Those will widely vary from organization to organization.
How much does a business engineer make?
By running a search on Glassdoor for Business Engineer, the average salary can go from $64k per year for smaller organizations to senior Business Intelligence Engineer at eBay and Facebook, for $117k and $140k of yearly base salary respectively.
A new discipline?
Business Engineering as a foundational discipline of the FourWeekMBA Curriculum
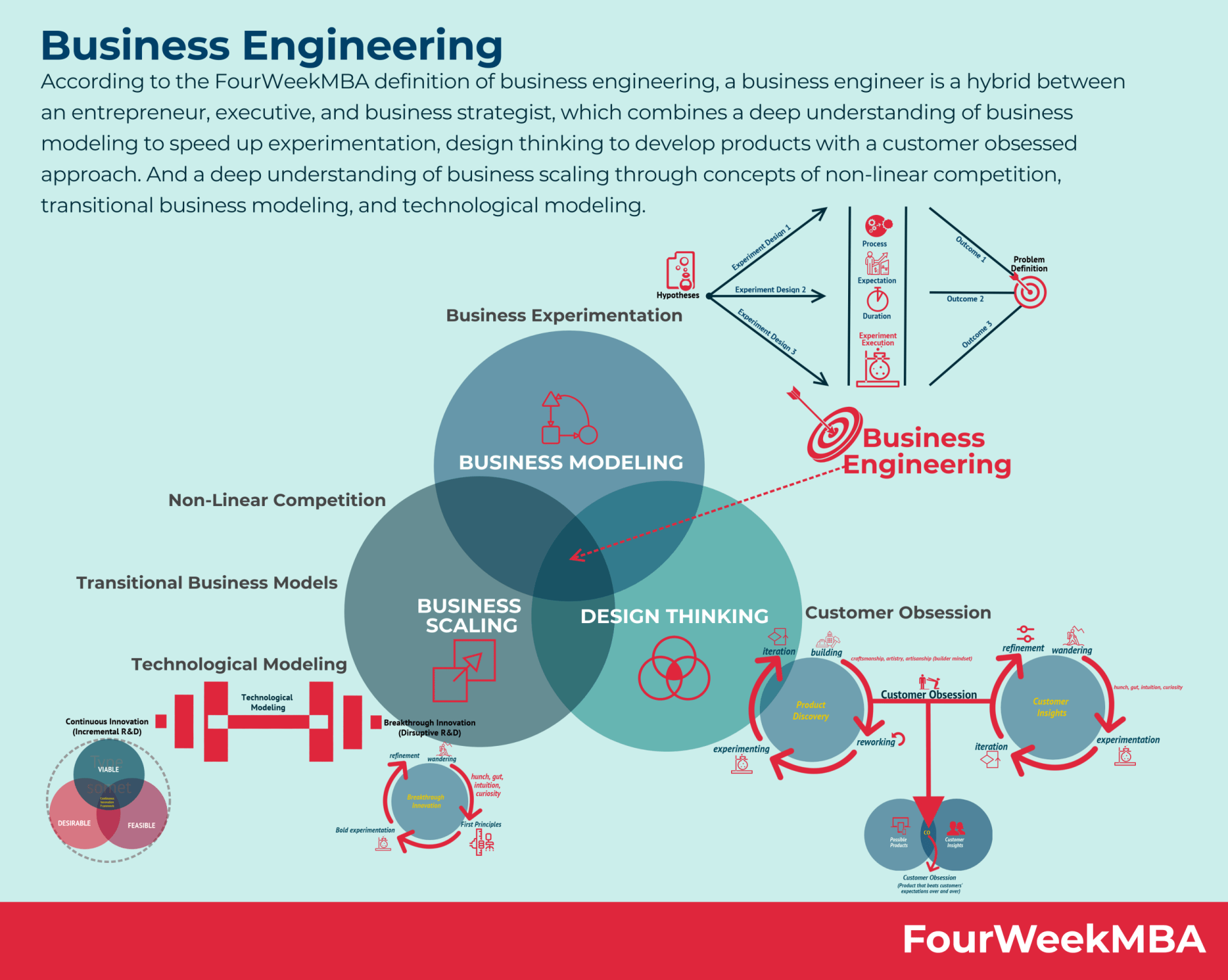

I argue that the next step to the evolution of business innovation is that of Business Engineering, usually intended as a person using technology to build technical processes within the organization.
However, in the FourWeekMBA view, the Business Engineer is a hybrid between an entrepreneur, a customer-centered business designer, and a business analyst, able to prevent false patterns, thus growing the business with a mixture of intuition, business acumen, testing, and experimentation.
While for many, business engineering is something more technical connected to attaching technology to business processes.
To me, that is more conceptual, and it stands for an understanding of the business world that comes from various disciplines.
In fact, the business engineer borrows experimentation from business modeling:


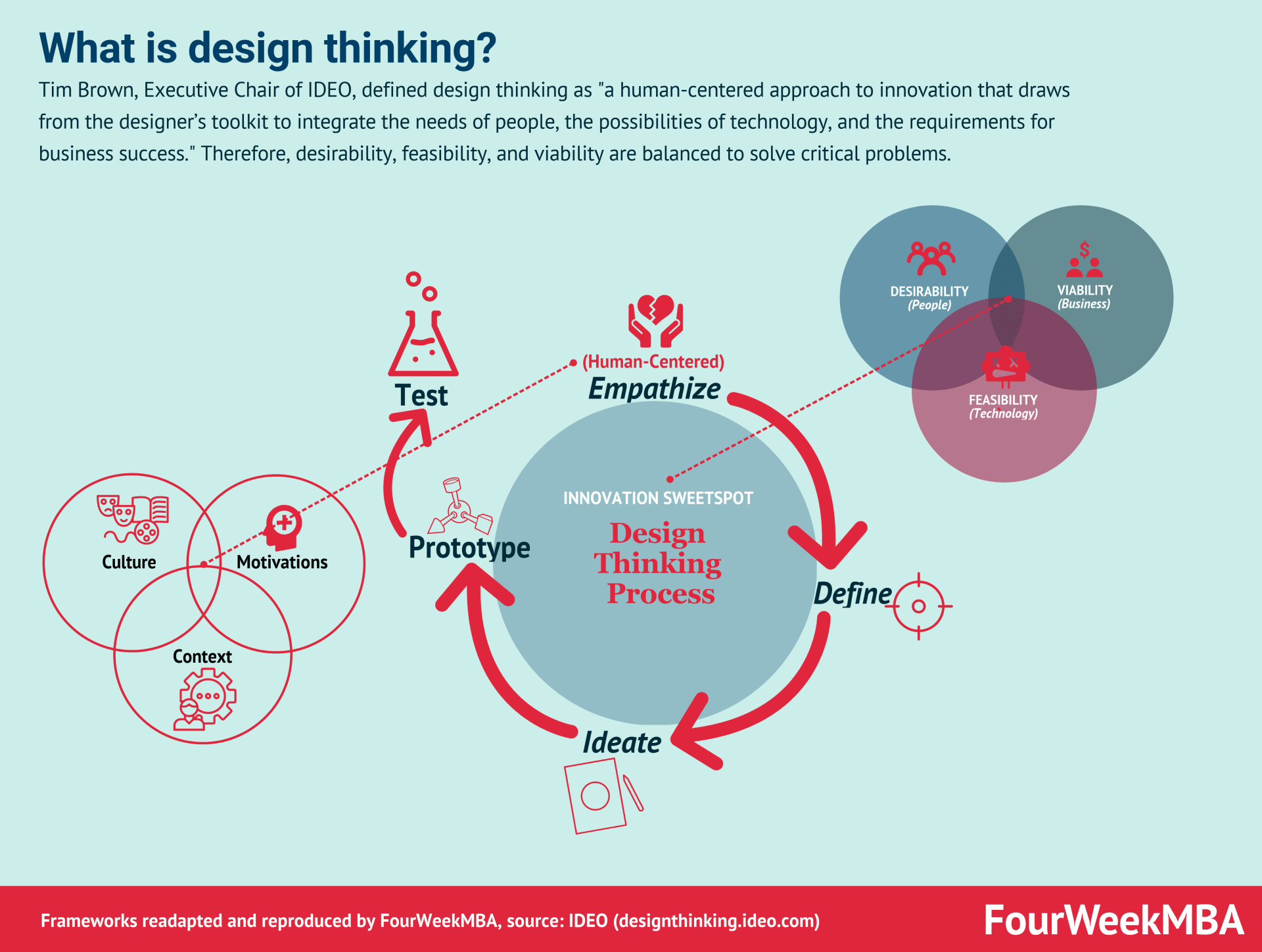
It borrows a customer-centered approach from design thinking:

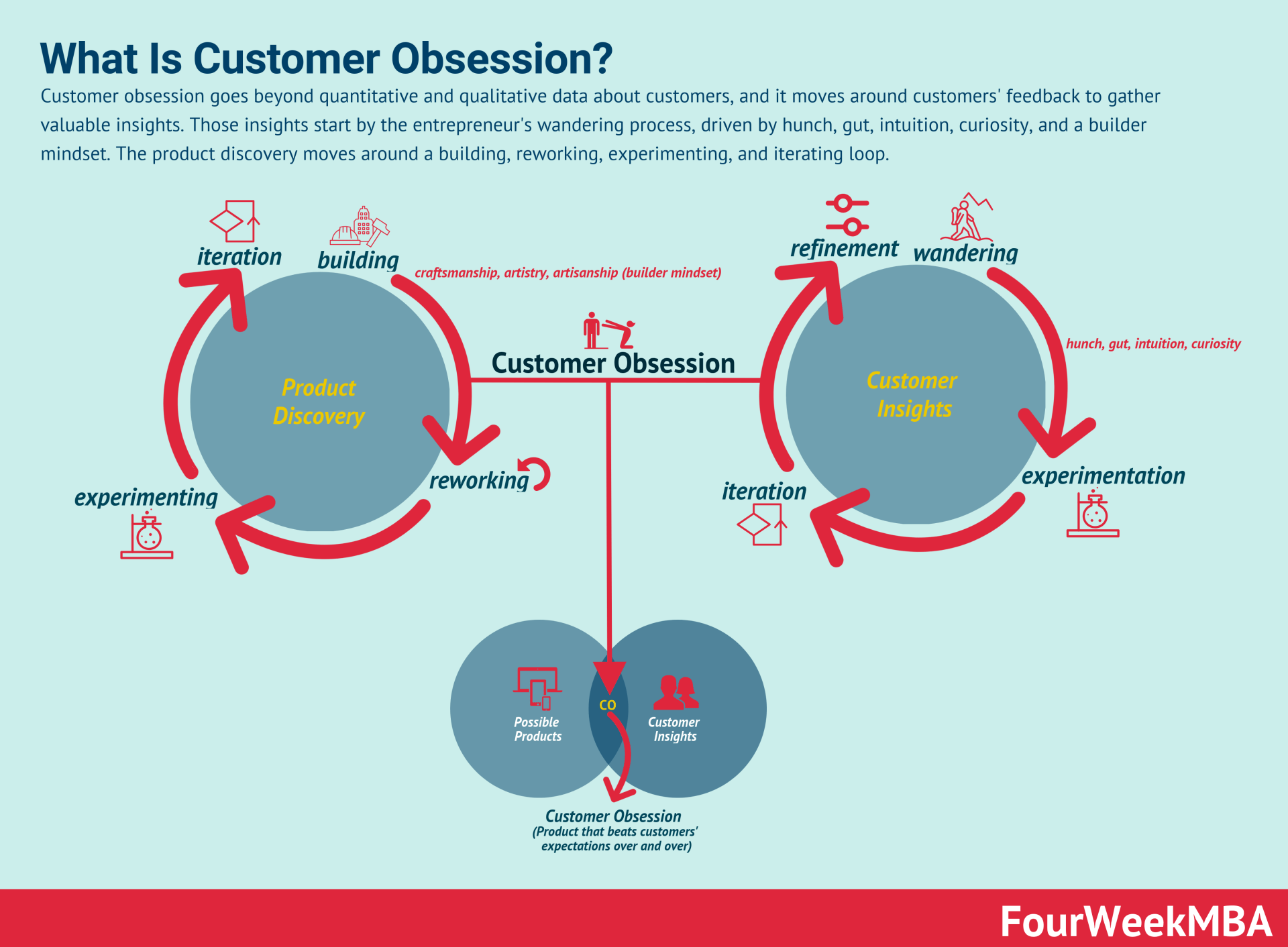
At the same time, it brings it to the next level with customer obsession:

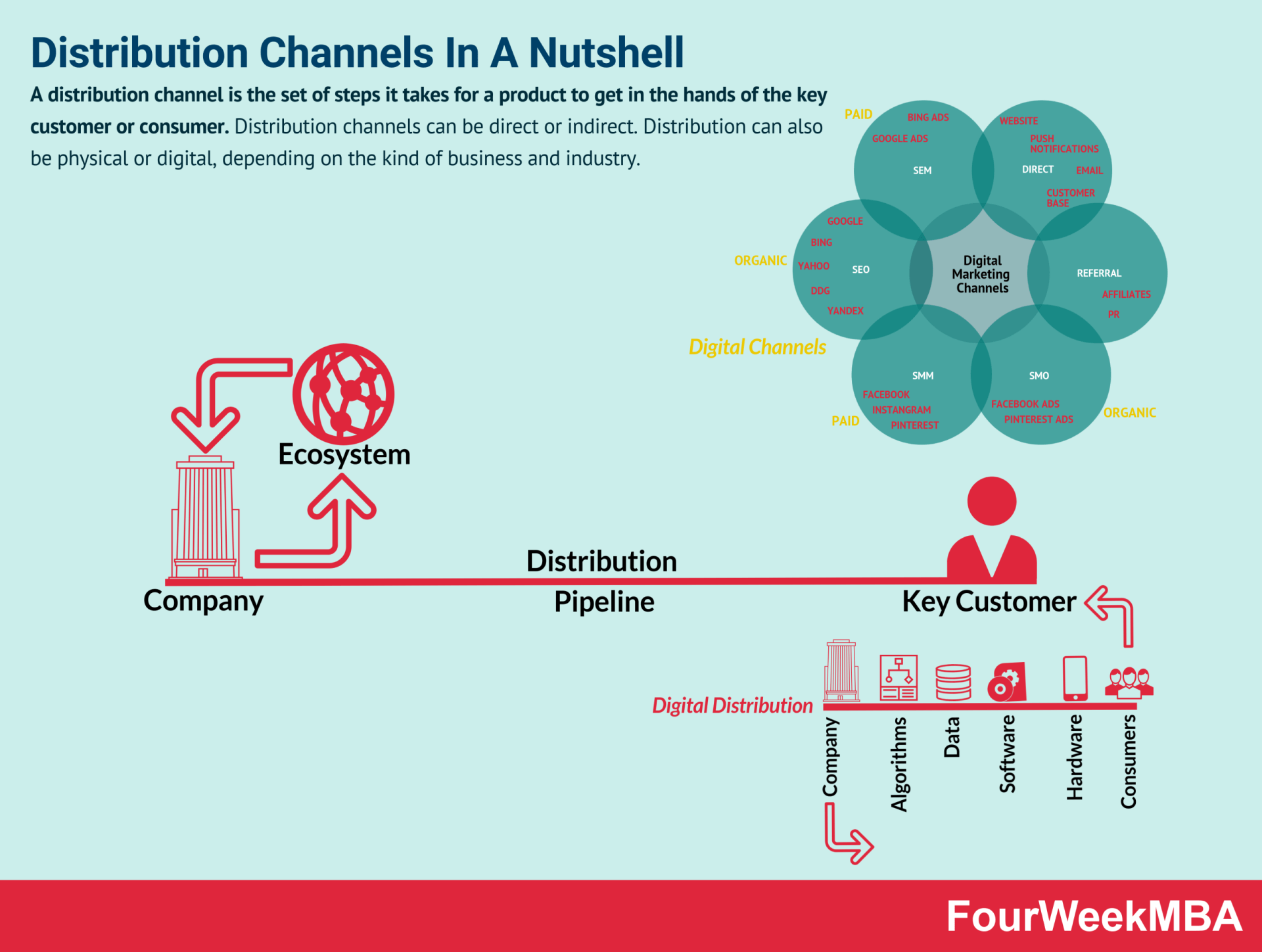
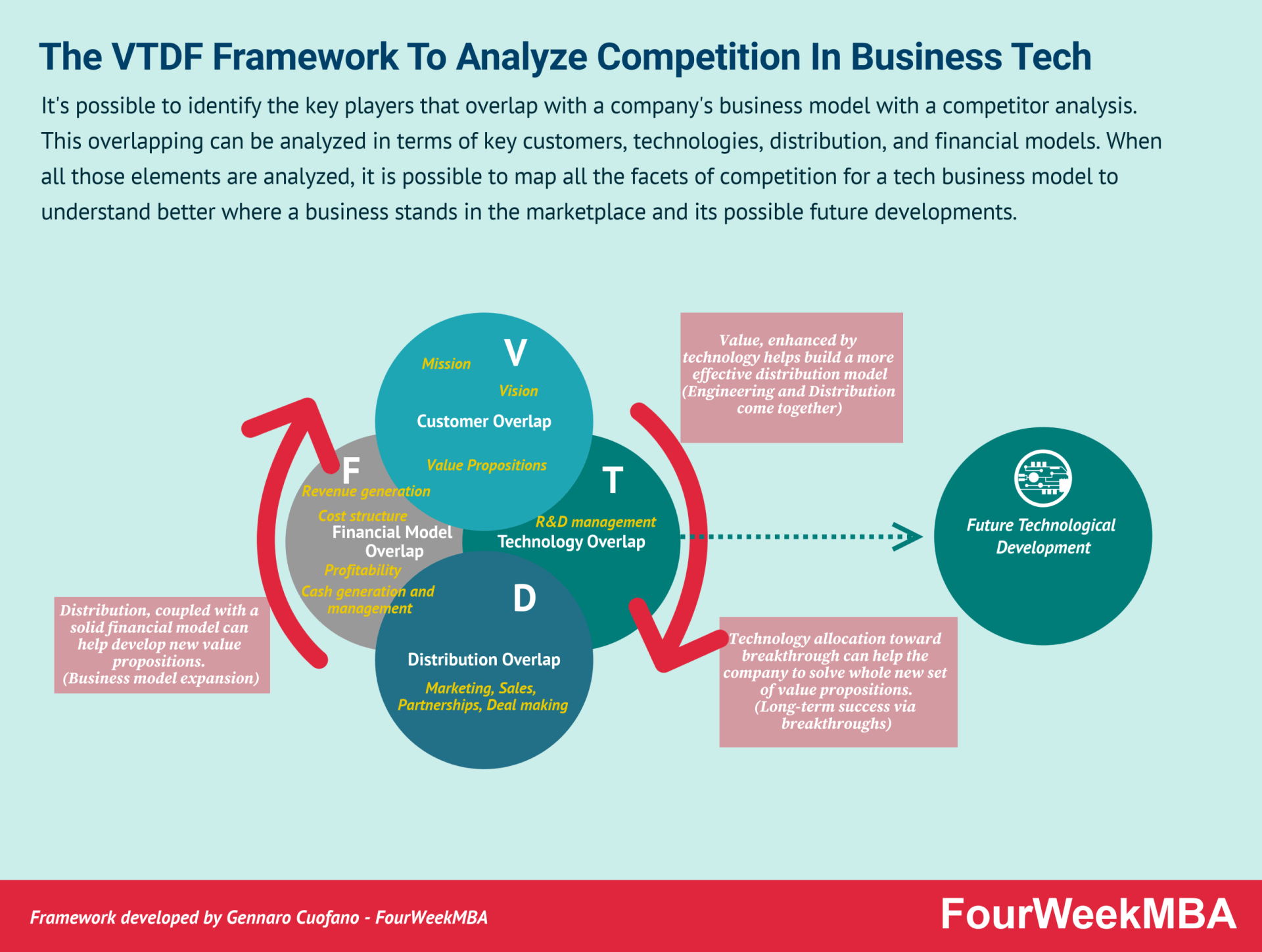
And all of that, while understanding the distribution model:

And financial model:

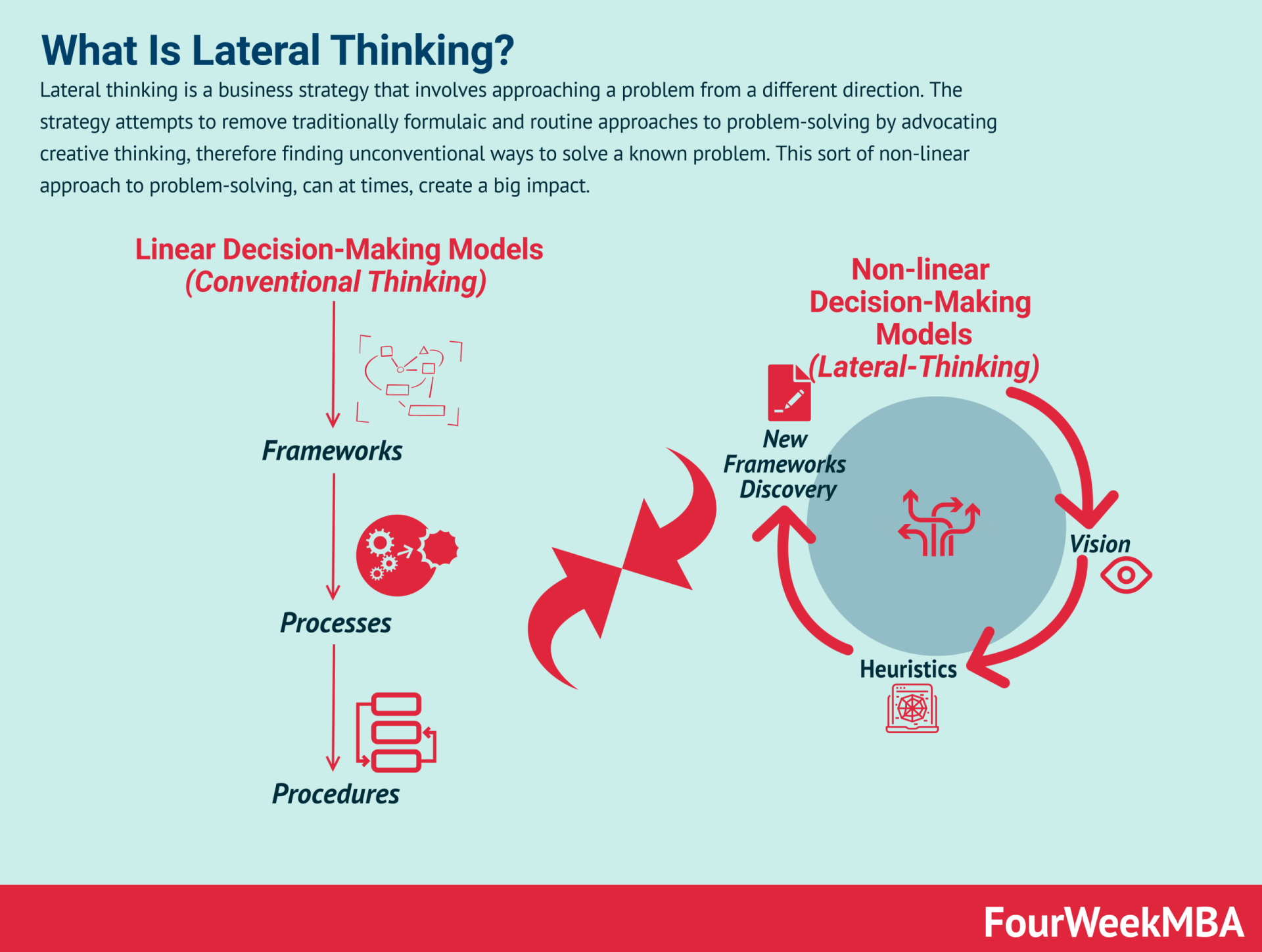
But most of all, the business engineer understands the difference between linear and non-linear thinking and knows when to apply one or the other:

Indeed, the business engineer knows that in a context of continuous, linear improvement, linear thinking might work:

But also how to drive breakthrough innovation:
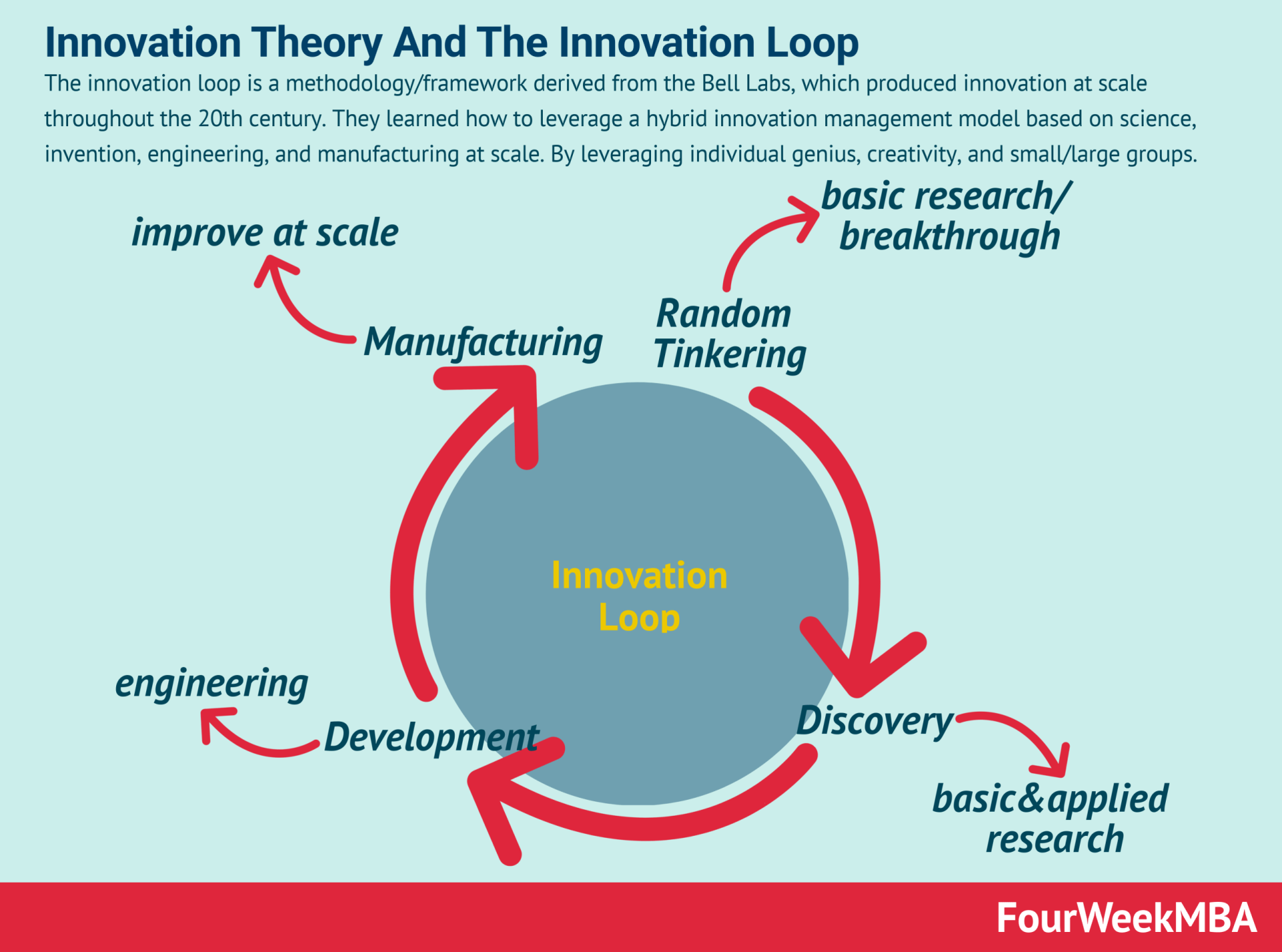

In what I like to call technological modeling or barbelling:
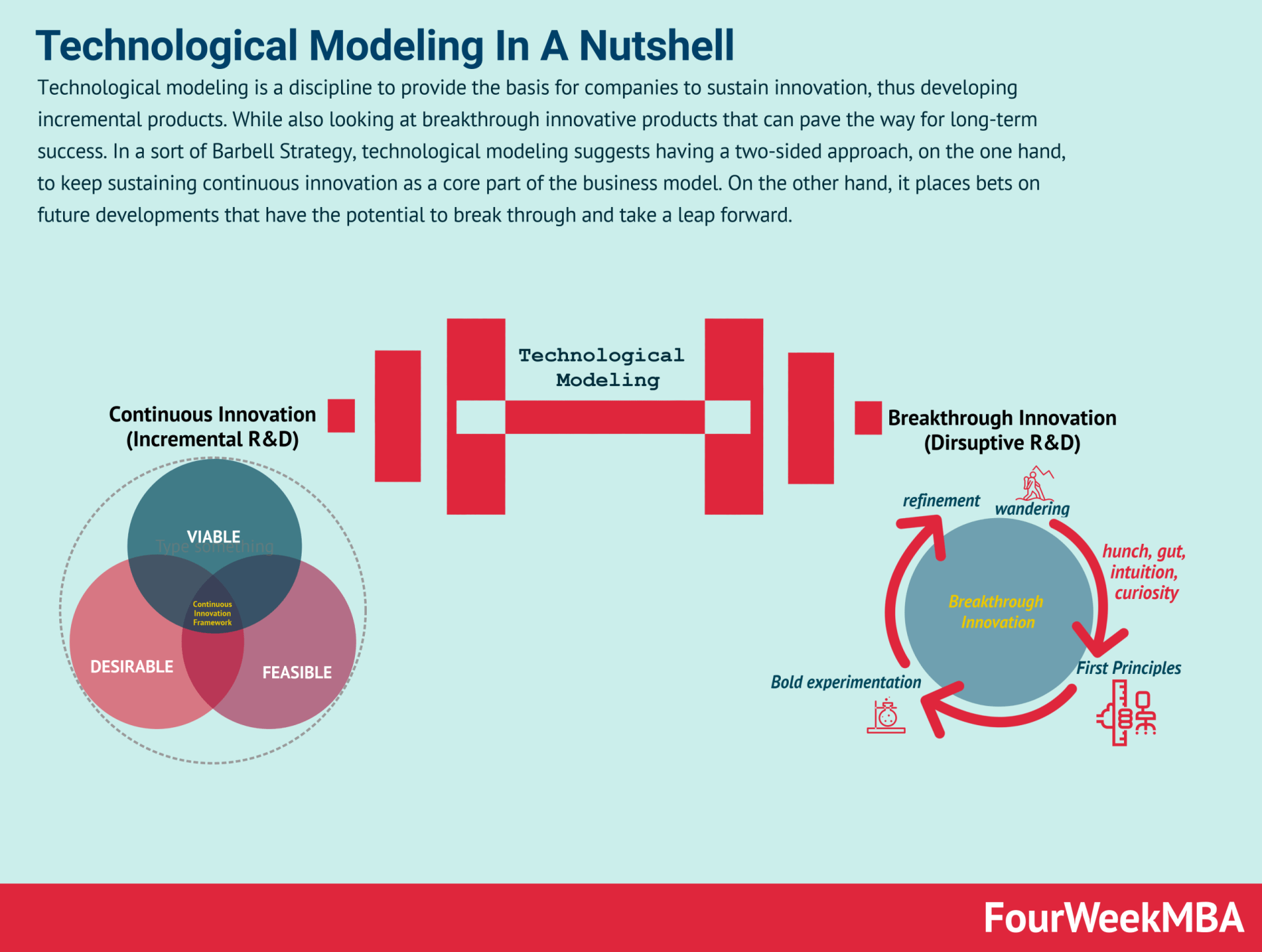

So that business innovation isn’t driven anymore in siloed departments, but the walls between product and marketing/distribution are wrecked, to create bottom-up growth.
Financial Modeling

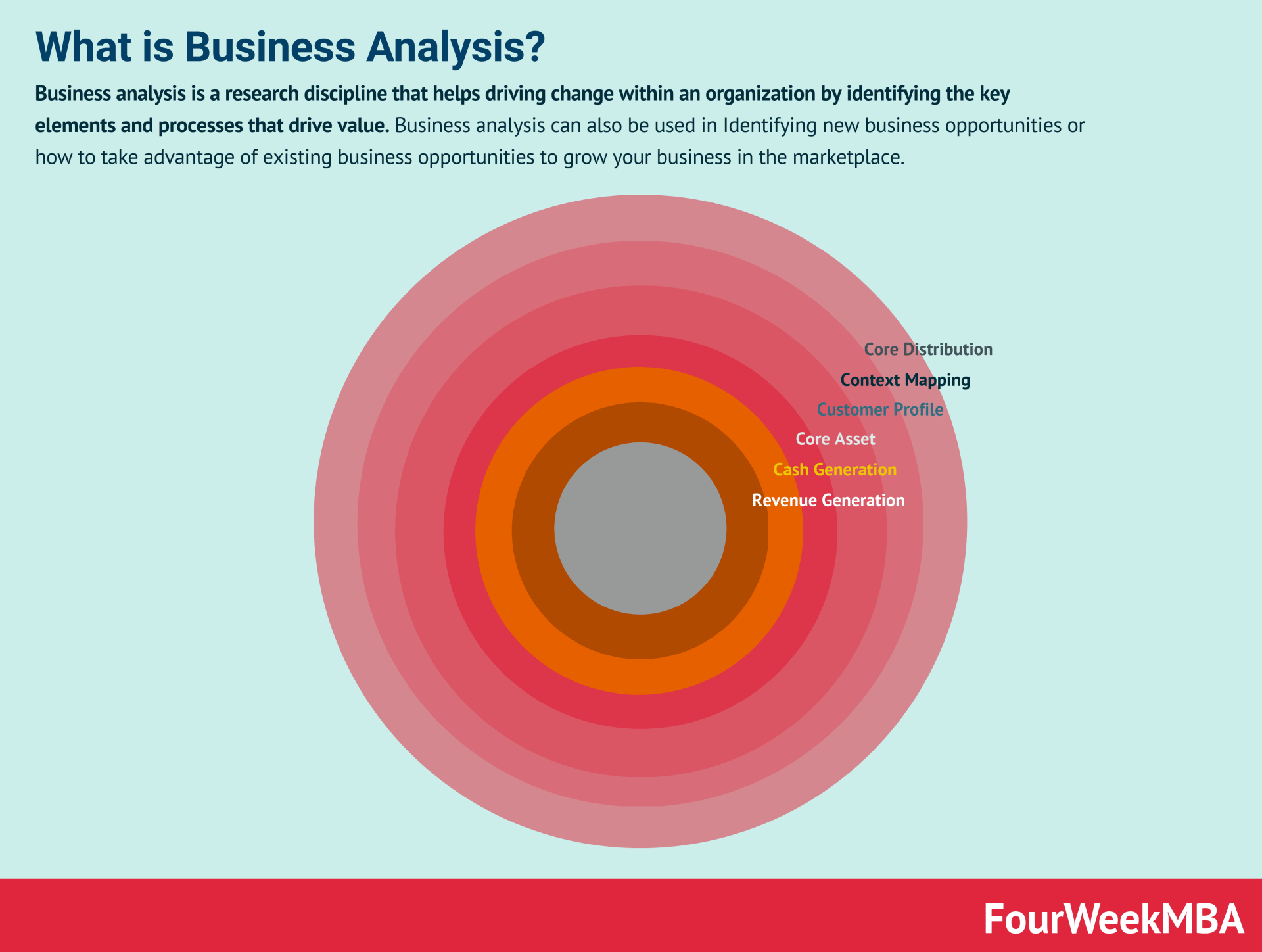
Business Analysis

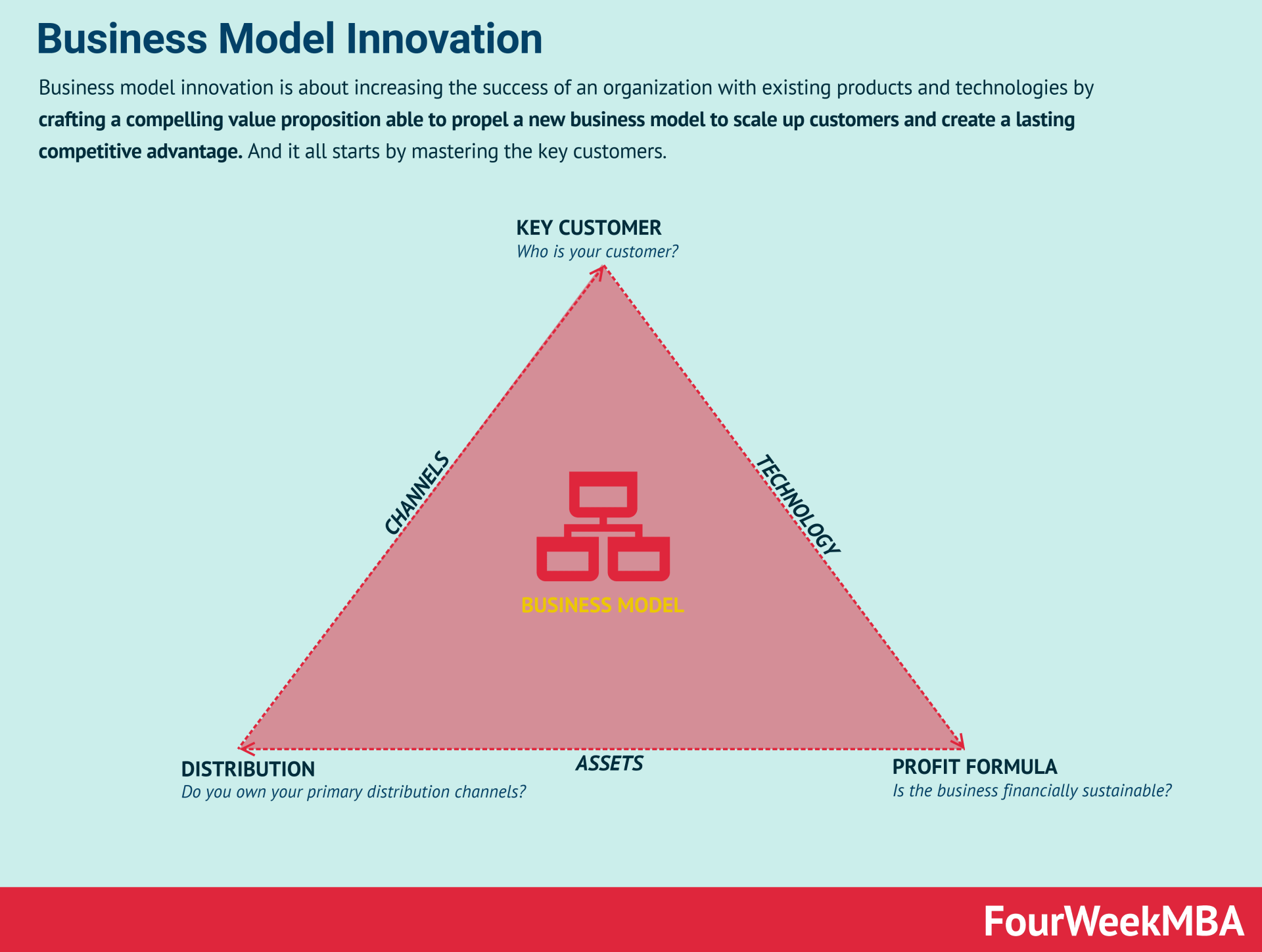
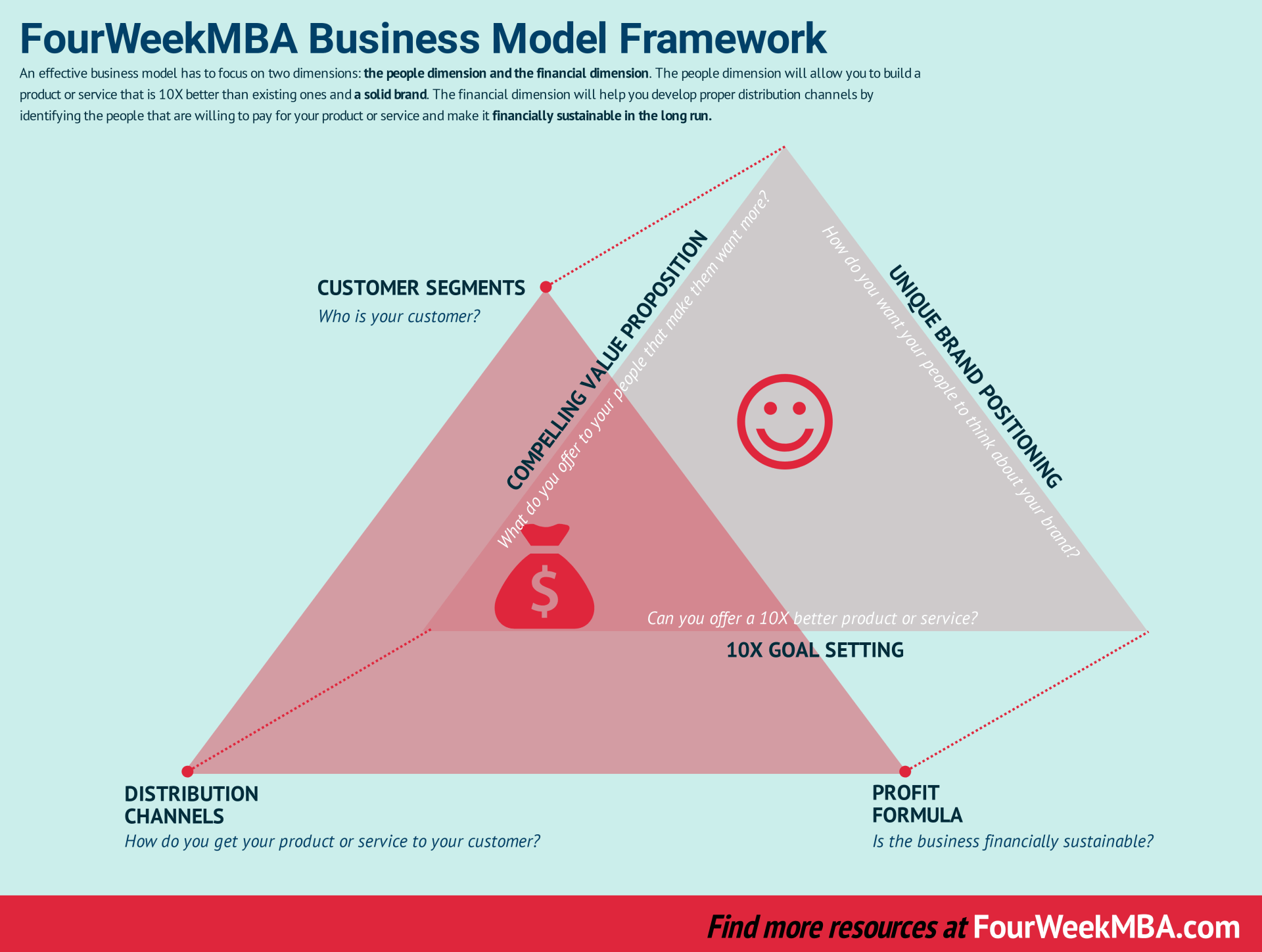
Business Modeling


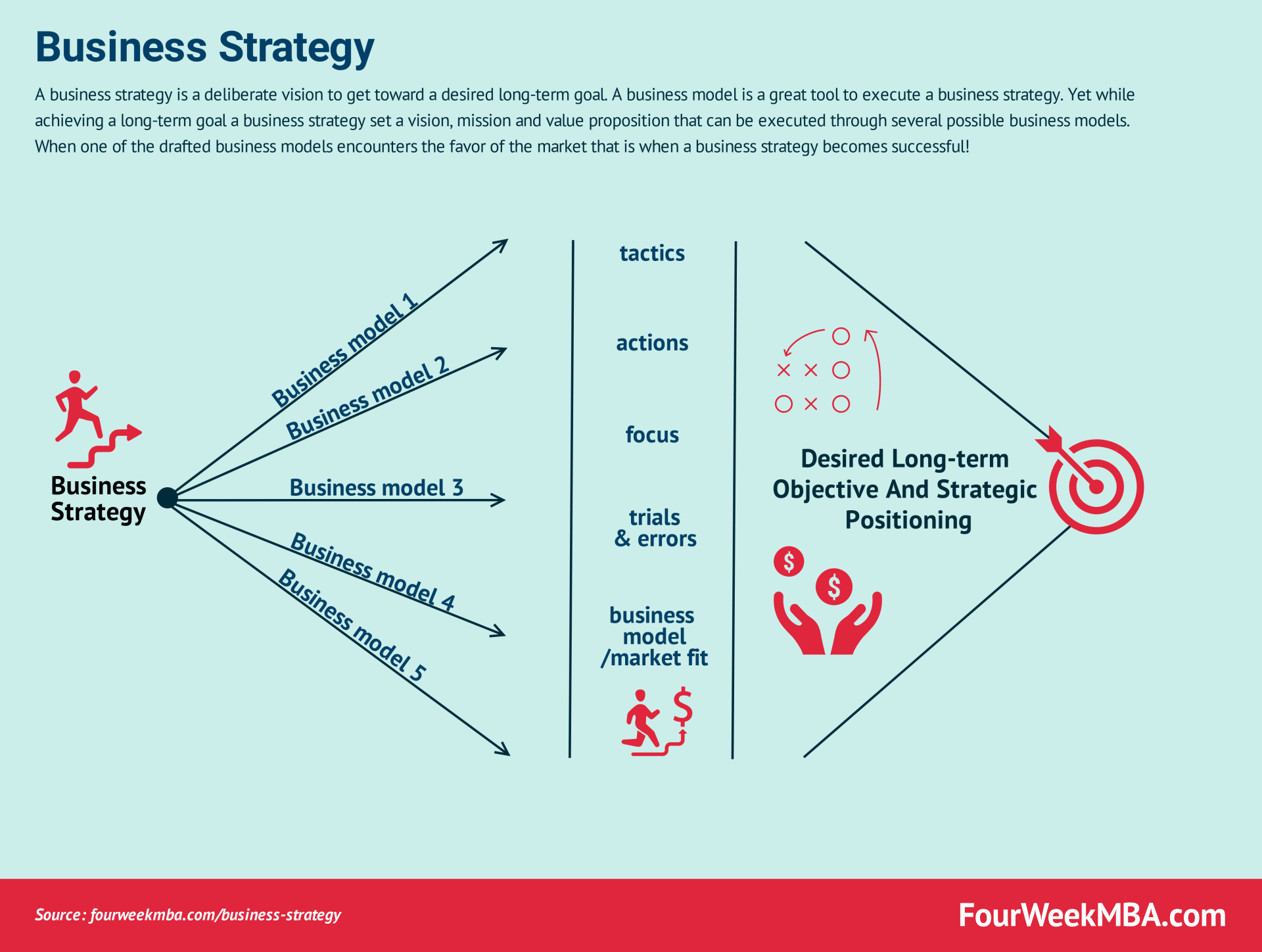

Technological Modeling


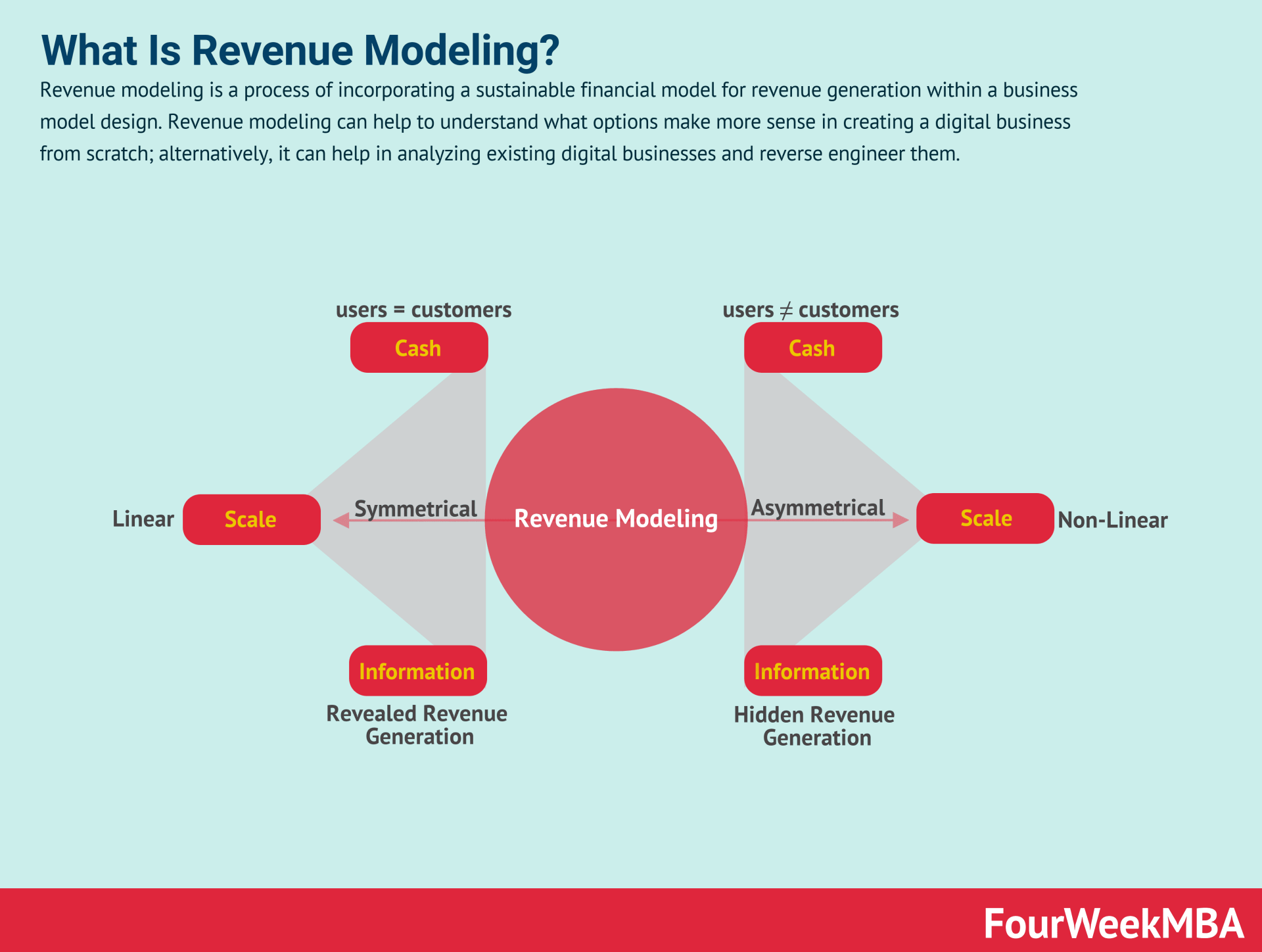
Revenue Modeling

Intution, guts, wandering and customer obsession


Do you want to become a business engineer? Start from the resources below:












